The landscape of motion sensing technology has made significant strides with the introduction of Wi-Fi sensing, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible using inexpensive devices like the ESP32 boards. A fascinating development in this realm is the ability of these gadgets to act as through-wall radars, effectively detecting movement and even subtle activities such as breathing, all while using Wi-Fi signals. This has opened up a plethora of opportunities for developers and hobbyists alike who are keen on creating advanced motion detection systems without the need for costly hardware.
Historically, motion detection relied heavily on passive infrared (PIR) sensors, which had their limitations, particularly when it came to detecting minimal movements. However, with advancements in Wi-Fi sensing, it’s now possible to leverage cheap, accessible components to achieve high-precision presence detection. For instance, the ESP32 series microcontrollers, including the ESP32, ESP32-S2, and ESP32-C3, can now capture minute movements caused by breathing or chewing. This level of sensitivity paves the way for a new era of smart environments where devices respond intuitively to human presence.
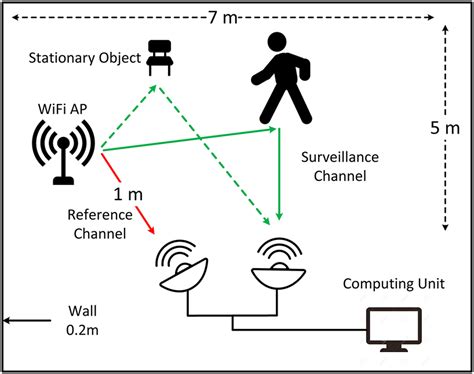
A key advantage of Wi-Fi sensing is its ability to function through walls, which significantly enhances its utility in home automation scenarios. Consider the implementation of systems that can monitor the presence of individuals in different rooms, adjusting lighting and climate control accordingly. This aspect not only improves energy efficiency but also personalizes the user experience. Combining a $3 ESP chip with a Wi-Fi CSI (Channel State Information) radar, anyone can build a robust presence detection system under $20.
With AI and machine learning becoming integral to modern technology, Wi-Fi sensing can be enhanced further. The integration of AI/Neural Processing Unit (NPU) in upcoming laptops from Intel and Qualcomm equipped with Wi-Fi 7 promises to offer a remarkable boost in on-device inference capabilities. These advances will allow devices to identify human activities with greater accuracy, combining RF radar and real-time AI processing. This trend is not just limited to personal gadgets but extends to broader commercial applications such as smart offices and healthcare monitoring.
The healthcare sector stands to benefit significantly from these non-invasive monitoring systems. Wi-Fi sensing can be employed to track vital signs like heart rate and respiratory patterns without the need for wearable devices. Research and products like the under-mattress sleep trackers have already demonstrated that even minute physiological changes can be monitored passively. For instance, Intel’s research into using Wi-Fi for respiration detection is pushing the boundaries of non-contact health monitoring, potentially leading to early detection of medical conditions based solely on changes in breathing patterns.
However, the adoption of these technologies raises questions about safety and privacy. While the power levels used by these devices are quite low, comparable to everyday Wi-Fi routers, there is still a cautious sentiment about continuous exposure, especially in sensitive environments like bedrooms. Users should be informed and confident in the safety profiles of these devices. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)’s stance on using Wi-Fi for respiratory monitoring reinforces that with proper standards and regulations, these innovations can be safe and effective.
In conclusion, the future of motion detection and human activity recognition is being reshaped by innovations in Wi-Fi sensing. The ease of integration with existing systems and the low-cost entry point make this technology incredibly accessible to a wide range of users, from hobbyists to professionals. As AI continues to drive advancements in this field, the applications will only become more diverse and impactful. For those looking to experiment, starting with an ESP32 board and exploring resources like the Awesome Wi-Fi CSI Sensing GitHub repository is a great way to dive into this transformative technology.

Leave a Reply